Fenugreek Gum, Guar Gum, and Xanthan Gum: Comparison Uses for Agriculture (2026)
/Agriculture uses for various gums like Fenugreek gun, Guar Gum, and Xanthan Gum
Below is a clear, practical comparison of fenugreek gum vs. guar gum vs. xanthan gum, specifically focusing on agricultural uses like soil amendments, seed coatings, biofertilizer carriers, and controlled-release systems.
Comparison of Fenugreek Gum, Guar Gum, and Xanthan Gum)
Overview Table (Quick Comparison of Fenugreek Gum, Guar Gum, and Xanthan Gum)
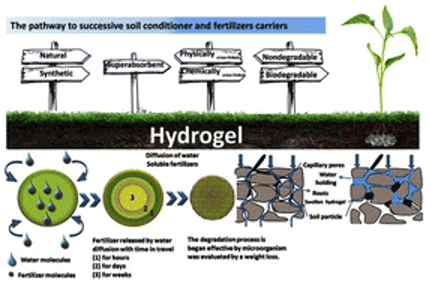
1. Soil Moisture Retention & Soil Conditioning
Excellent water-binding; forms elastic, uniform hydrogel
Less prone to brittleness compared to guar
Ideal for high-value crops or arid soils
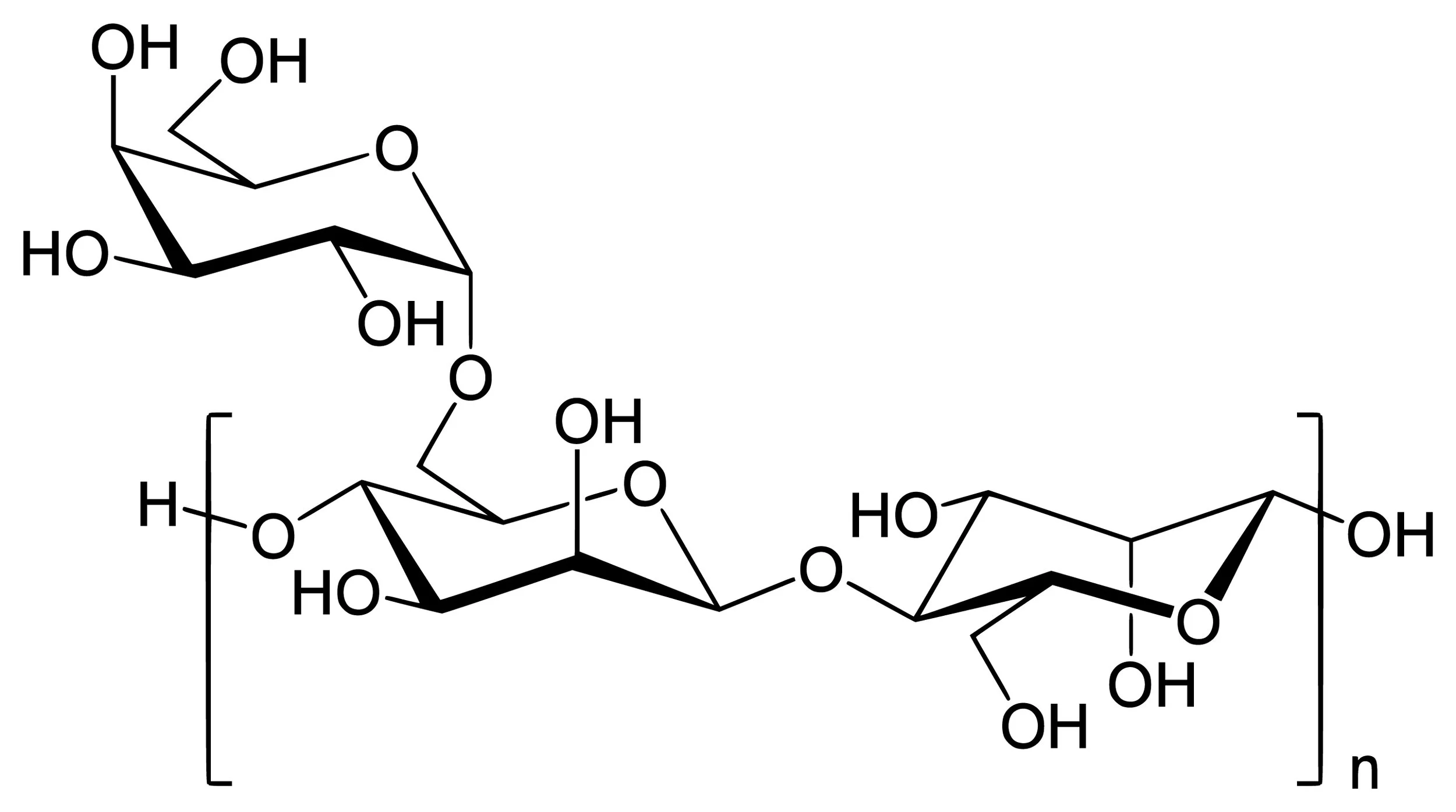
Fenugreek Gum polysaccharides
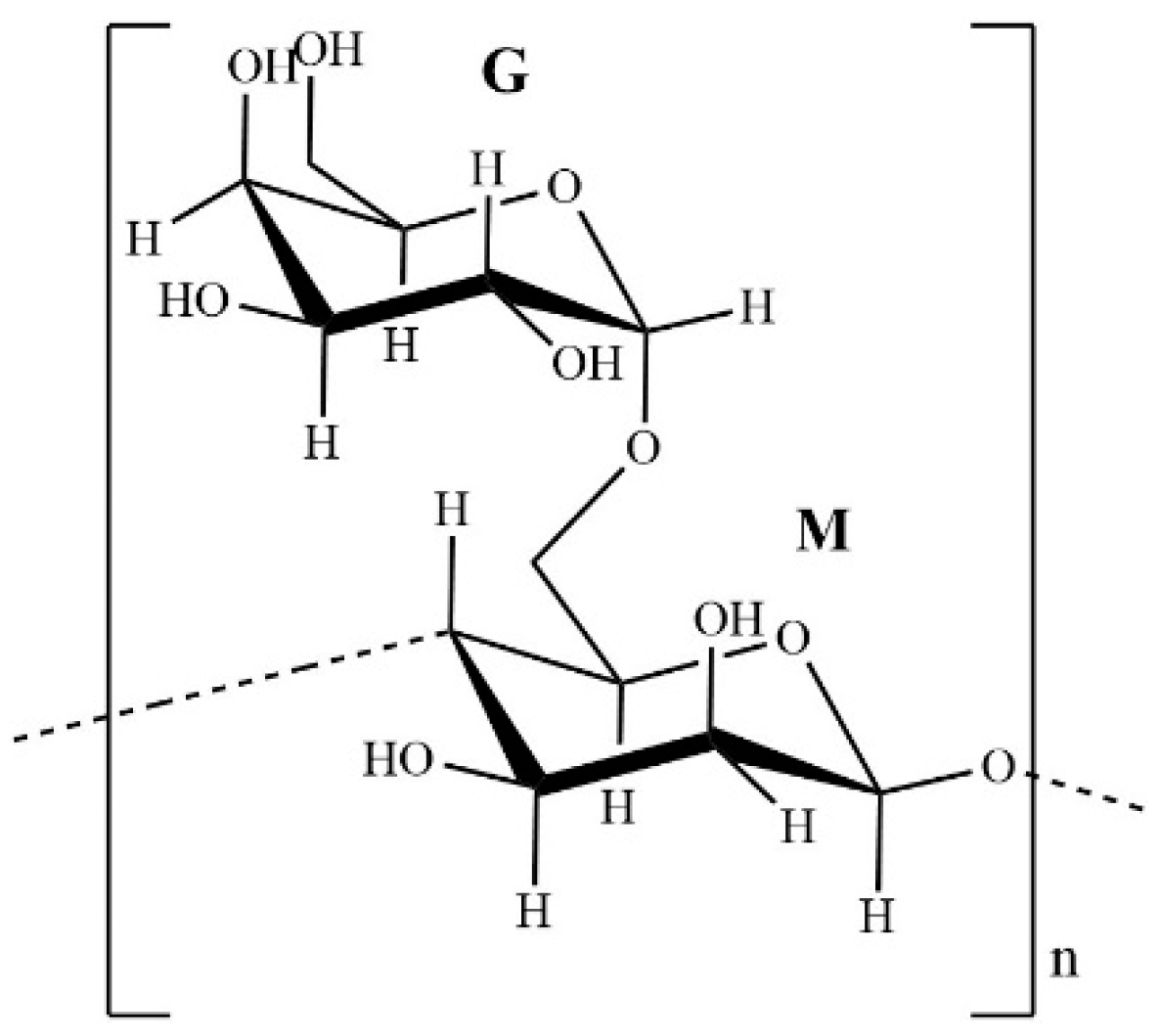
Best for large-scale soil amendments due to low cost
High viscosity, but creates more brittle gels
Widely used in hydro-seeding and water retention blends
Guar Gum Molecular Structure
Very stable under saline, alkaline, or hot conditions
More expensive for large-scale soil application
Typically blended with cheaper gums for cost-effectiveness
XANTHAN Gum Molecular Structure
Winner for Soil Conditioning:
Cost-efficient bulk use: Guar gum
Performance-focused use: Fenugreek gum
Extreme conditions: Xanthan gum
🔍 2. Seed Coating & Pelleting
Fenugreek Gum
Strong natural bio-adhesive
Smooth, uniform coating films
Excellent for precision pelleting and microbial inoculant adhesion
Fenugreek Gum FOR Seed Coating & Pelleting
Guar Gum
Good binder, widely used due to low price
Can form clumpy coatings if not processed carefully
Xanthan Gum
Very sticky and stable
Excellent for heavy-duty pelleting, but higher cost limits usage
Winner for Seed Coating and Pelleting:
Premium-quality seed coating: Fenugreek
Low-cost, large-scale pelleting: Guar
High-strength pellets (e.g., pellets + insecticides): Xanthan
Agriculture and gum usage
🔍 3. Carrier for Biofertilizers & Beneficial Microbes
Fenugreek Gum
Biofriendly environment for microbes
Good moisture retention enhances microbial survival
Forms stable microcapsules
Guar Gum
Also good but slightly less stable under acidic/alkaline conditions
Xanthan Gum
Excellent for encapsulation systems, especially when fermented with other polysaccharides
Highest stability under stress
Carrier for Biofertilizers and Beneficial Microbes Winner:
General use: Fenugreek
Industrial-scale carriers: Guar
High-performance encapsulation: Xanthan
Agriculture and gum benefits
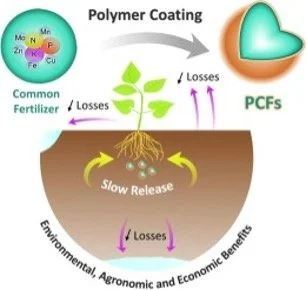
🔍 4. Controlled-Release Fertilizers/Pesticides (CRFs & CRPs)
Polymer Coating Diagram
Fenugreek Gum
Forms biodegradable films suitable for moderate release rates
Good for eco-friendly CRF coatings
Hydrogel Diagram for Agriculture Gum Usage
Guar Gum
Slower biodegradation and more brittle films
Often blended with other gums
Xanthan Gum
Best rheological stability
Allows precise control of release timing
Excellent for encapsulating pesticides or micronutrients
Controlled-Release Fertilizer/Pesticides (CRFs & CRPs) Winner: Xanthan gum for advanced controlled-release systems.
fenugreek powder used for gum production in agriculture use
🔍 5. Compatibility with Fertilizers and Agrochemicals
Fenugreek Gum
Good compatibility, but may show slight viscosity drop in very high-salt environments
Guar Gum
Poor salt tolerance → Rapid viscosity loss
Not ideal with fertilizers rich in Ca/Mg salts
Xanthan Gum
Best salt and pH tolerance; remains stable in:
Urea
NPK solutions
Micronutrient foliar sprays
Saline irrigation water
Compatible with Fertilizers and Agrochemicals Winner: Xanthan gum
Guar plant used for Agriculture gum
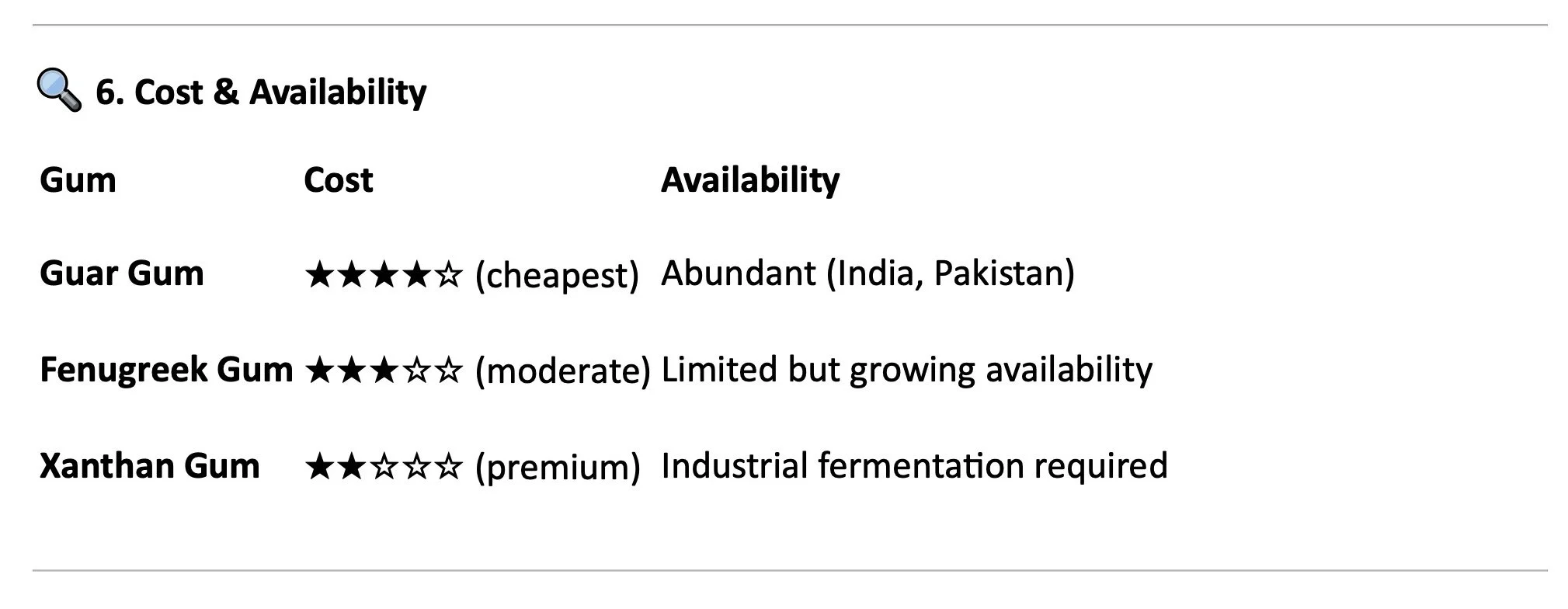
🔍 6. Cost & Availability
🎯 Summary: When to Choose Which Gum
✔ Choose Fenugreek Gum if you need:
Premium seed coating
Moisture management for high-value crops
Carrier for beneficial microbes
Biodegradable thickener for organic farming
Fenugreek field for creating gum for agriculture implementations; Fenugreek located in Avonlea, Saskatchewan Canada 2025
✔ Choose Guar Gum if you need:
Cheapest option for soil conditioners
Large-scale seed treatments
Bulk hydroseeding / erosion control mixtures
✔ Choose Xanthan Gum if you need:
Stability under salinity, heat, or pH extremes
Controlled-release fertilizers/pesticides
High-strength gel systems
Stable agricultural sprays